Which of the following defines key usage with regard to standard extensions? ✅ Tốt
Kinh Nghiệm về Which of the following defines key usage with regard to standard extensions? Chi Tiết
Dương Anh Tuấn đang tìm kiếm từ khóa Which of the following defines key usage with regard to standard extensions? được Update vào lúc : 2022-12-26 04:40:20 . Với phương châm chia sẻ Thủ Thuật Hướng dẫn trong nội dung bài viết một cách Chi Tiết 2022. Nếu sau khi Read tài liệu vẫn ko hiểu thì hoàn toàn có thể lại Comment ở cuối bài để Tác giả lý giải và hướng dẫn lại nha.The Netscape Certificate Type extension can be used to limit the purposes for which a certificate can be used. It has been replaced by the X.509 v3 extensions and , but must still be supported in deployments that include Navigator 3.x clients.
Nội dung chính Show- Extended key usageX.509 certificate fieldsApplications of X.509 certificatesBenefits of X.509 certificatesHistory of X.509 certificatesWhich of the following is a standard format for digital certificates?Which standard is most widely used for certificates?What is a HSM used for quizlet?What extension field is used with a web server certificate to support the identification of the server by multiple specific subdomain labels group of answer choices?
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.13
DiscussionThe value of this extension is an IA5String. It is a comment that can be displayed to the user when the certificate is viewed.
This document explains how to validate a certificate’s purpose before you upload the certificate to a keystore or a truststore. The process relies on OpenSSL for validation and is applicable on any environment where OpenSSL is available.
The TLS certificates are generally issued with one or more purposes for which they can be used. Typically this is done to restrict the number of operations for which a public key contained in the certificate can be used. The purpose of the certificate is available in the following certificate extensions:
- Key usageExtended key usage
Key usage
The key usage extension defines the purpose (for example, encipherment, signature, or certificate signing) of the key contained in the certificate. If the public key is used for entity authentication, then the certificate extension should have the key usage Digital signature.
The different key usage extensions available for a TLS certificate created using the Certificate Authority (CA) process are as follows:
- Digital signatureNon-repudiationKey enciphermentData enciphermentKey agreementCertificate signingCRL signingEncipher onlyDecipher only
For more information on these key usage extensions, see .
Extended key usage
This extension indicates one or more purposes for which the certified public key may be used, in addition to or in place of the basic purposes indicated in the key usage extension. In general, this extension will appear only in end entity certificates.
Some common extended key usage extensions are as follows:
- TLS Web server authenticationTLS Web client authenticationanyExtendedKeyUsage
An extended key can be either critical or non-critical.
- If the extension is critical, the certificate must be used only for the indicated purpose or purposes. If the certificate is used for another purpose, it is in violation of the CA's policy.If the extension is non-critical, it indicates the intended purpose or purposes of the key is informational and does not imply that the CA restricts use of the key to the purpose indicated. However, applications that use certificates may require that a particular purpose be indicated in order for the certificate to be acceptable.
If a certificate contains both the key usage field and the extended key usage field as critical then both fields must be processed independently, and the certificate can be used only for a purpose that satisfies both key usage values. However, if there is no purpose that can satisfy both key usage values, then that certificate must not be used for any purpose.
When you procure a certificate, ensure that it has the proper key usage defined to satisfy the requirements for client or server certificates without which the TLS handshake would fail.
An X.509 certificate is a digital certificate that uses the widely accepted international X.509 public key infrastructure (PKI) standard to verify that a public key belongs to the user, computer or service identity contained within the certificate.
A public key is a large numerical value used to encrypt data or check the legitimacy of a digital signature. A PKI, moreover, is the underlying framework that enables entities like users and servers to securely exchange information using digital certificates.
The X.509 certificate is a safeguard against malicious network impersonators. When a certificate is signed by a trusted authority, or is otherwise validated, the device holding the certificate can validate documents. It can also use a public key certificate to secure communications with a second party.
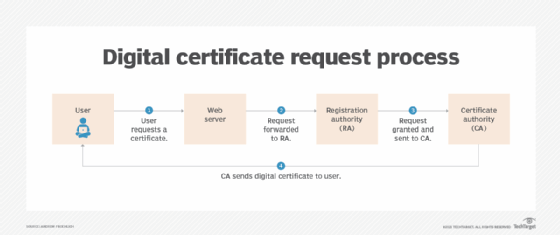 Digital certificates must be requested from a registration authority and granted by a certificate authority.
Digital certificates must be requested from a registration authority and granted by a certificate authority.The X.509 certificate is defined by the International Telecommunication Union's Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T).
In cryptography, the X.509 certificate securely associates cryptographic key pairs of public and private keys with websites, individuals or organizations. The certificate is typically used to manage identity and security in computer networking and over the internet. For the internet, it is used in numerous protocols to ensure a malicious website doesn't fool a web browser. The X.509 certificate is also used to secure email, device communications and digital signatures.
The X.509 standard is based on Abstract Syntax Notation One, an interface description language. An X.509 certificate contains an identity and a public key. It binds an identity -- such as an individual or hostname -- to a public key with a digital signature. The signature is either made by a trusted certificate authority (CA) or is self-signed. Some digital certificates can also be automated.
X.509 certificate fields
An X.509 certificate contains information about the identity to which the certificate is issued and the identity that issued it. Standard information in an X.509 certificate includes the following:
- Version. Which X.509 version applies to the certificate, indicating what data the certificate must include.Serial number. The CA creating the certificate must assign it a serial number that distinguishes the CA certificate from other certificates.Algorithm information. The signature algorithm the issuer uses to sign the certificate.Issuer distinguished name. The name of the entity issuing the certificate -- usually, the CA.Validity period of the certificate. The start and end date, as well as the time the certificate is valid and can be trusted.Subject distinguished name. The name to which the certificate is issued.Subject public key information. The public key associated with the identity.Extensions (optional). Extensions have their own unique IDs, expressed as a set of values called an object identifier. An extension can be rejected if it is not recognized or if the extension has information that can't be processed.
Applications of X.509 certificates
Common applications of X.509 certificates include the following:
- Digital identities. A key use of X.509 certificates can be to authenticate the digital identities of devices, people, data and applications.TLS/SSL and web browser security. PKI and X.509 are the basis for the Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols. Web browsers read the X.509 certificate of a webpage to verify its TLS/SSL status.
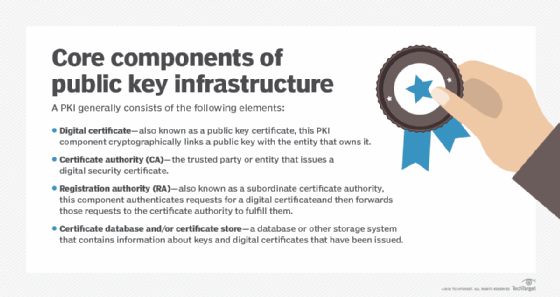 Public key infrastructure has four key components.Digital signatures and document signing. X.509 certificates can authenticate the identity of a digitally signed document, specifically authenticating both the signature and document.E-Mail certificates. Secure email standards -- for example, Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions, or S/MIME -- use X.509 certificates.Secure Shell keys. Secure Shell (SSH) keys are a form of X.509 certificate. They provide secure access credentials used in the SSH protocol.Code signing. Code signing uses certificates to authenticate code so end users can verify that code has not been altered by a third party.
Public key infrastructure has four key components.Digital signatures and document signing. X.509 certificates can authenticate the identity of a digitally signed document, specifically authenticating both the signature and document.E-Mail certificates. Secure email standards -- for example, Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions, or S/MIME -- use X.509 certificates.Secure Shell keys. Secure Shell (SSH) keys are a form of X.509 certificate. They provide secure access credentials used in the SSH protocol.Code signing. Code signing uses certificates to authenticate code so end users can verify that code has not been altered by a third party.Benefits of X.509 certificates
Potential benefits that come with X.509 certificates include the following:
- Wide area of use. X.509 certificates are a part of web browser security, web server security, online document signing, SSH keys and email security.Level of trust. Certificates help safeguard against potentially malicious network impersonators.How signed certificates are issued. Certificates are signed by a publicly trusted issuer, such as a CA, or self-signed.
History of X.509 certificates
The first X.509 certificates were issued in 1988 as part of the ITU-T and the X.500 directory services standard. The current version, version 9, was defined in October 2022.
As more versions came out, more certificate fields were added or refined. For example, in 1993, version 2 added two fields to support directory access control, as well as subject and issuer unique identifiers. The X.509 version 3 certificate was released in 1996 and defines the formatting used for certificate extensions. It also was used by the Internet Engineering Task Force in the development of its own X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and Certificate Revocation List, or CRL, Profile standard.
Learn about digital certificates and how an automated version of certificate management can help retain IT talent.
Which of the following is a standard format for digital certificates?
A. The X. 509 standard dictates digital certificate file format, as well as use and information contained in the file.Which standard is most widely used for certificates?
The most widely accepted format for certificates is X. 509. Because X. 509 is an International Standard, any application complying with X.What is a HSM used for quizlet?
What is an HSM? A hardware security module (HSM) is any type of system for performing cryptographic operations and storing key material securely. An HSM is usually provisioned as a network-connected appliance, but it could also be a portable device connected to a PC management station or a plugin card for a server.What extension field is used with a web server certificate to support the identification of the server by multiple specific subdomain labels group of answer choices?
What extension field is used with a web server certificate to support the identification of the server by multiple subdomain labels? The Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field. Tải thêm tài liệu liên quan đến nội dung bài viết Which of the following defines key usage with regard to standard extensions?